Chatbots
Anatomy
The following diagram outlines the primary components within the chatbot pattern.
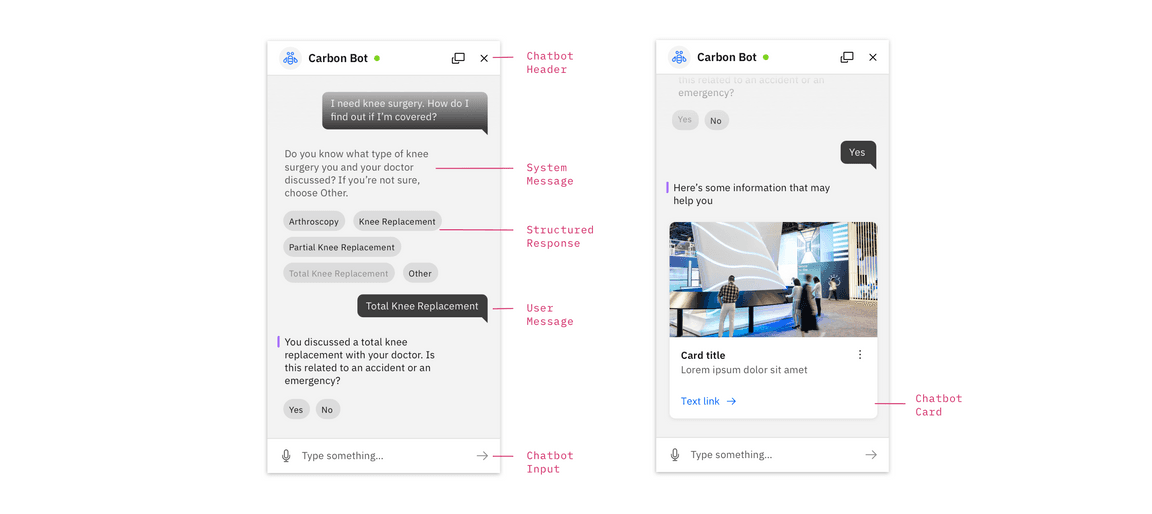
The chatbot header contains the title of the chat and up to four action buttons that control the chatbot application. Typically, the “close” icon must always be included.
- Default
- With avatar
- Large
System Messages represent the bot’s response to the user. Past messages will have a faded treatment, whereas active messages have an indicator applied (see below)
- Default
A user message indicates what the user has input via text input, structured response, or voice.
- Default
Structured responses present choices to the user that are easy for the bot to understand. When selected, a structured response will change its visual appearance and a user message will appear with the same content.
- Default
The Chatbot input is comprised of a text input field, a configurable button for other input (e.g., voice) and a submit button.
- Default
- Without action button
Launch buttons are the means by which a user initiates a conversation with your bot and are the first interaction of the bot experience.
- Primary
- Alternate
Cards are used to display more information (including text and images) about a significant action that a user can take. They can also be used to display text and image together for a purely informational purpose.
- Card with text (Hero)
- Card with text (Large)
- Card with text (Mini)
- Card with image (Avatar)
- Card with image (Large)
- Card with image (Mini)
- Card with data (Table)
- Card with data (Visualization)
Requesting information
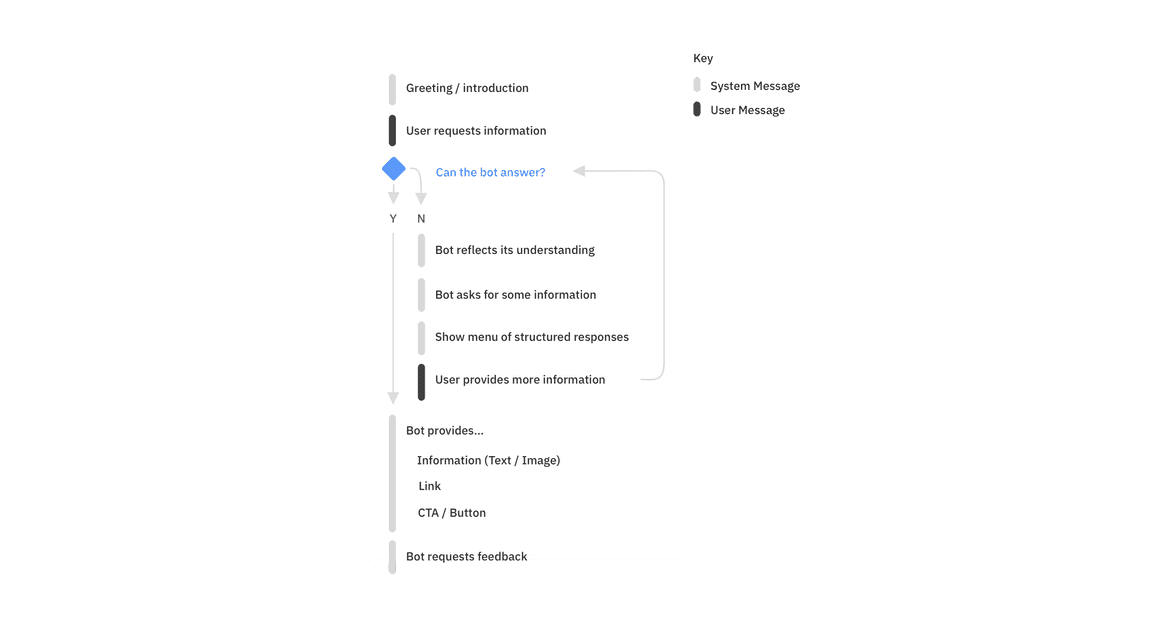
The following flow shows a typical exchange between a user and a bot. This model can be used as a baseline to start building useful conversational experiences.
Best practices
At a minimum, use these best practices to help ensure a successful conversational experience. For more in-depth conversational principles, see IBM Design for Conversational AI.
Introduction
Ensure your users know they are talking to a bot and that the bot has stated its purpose. Set the context for what questions users can ask about.
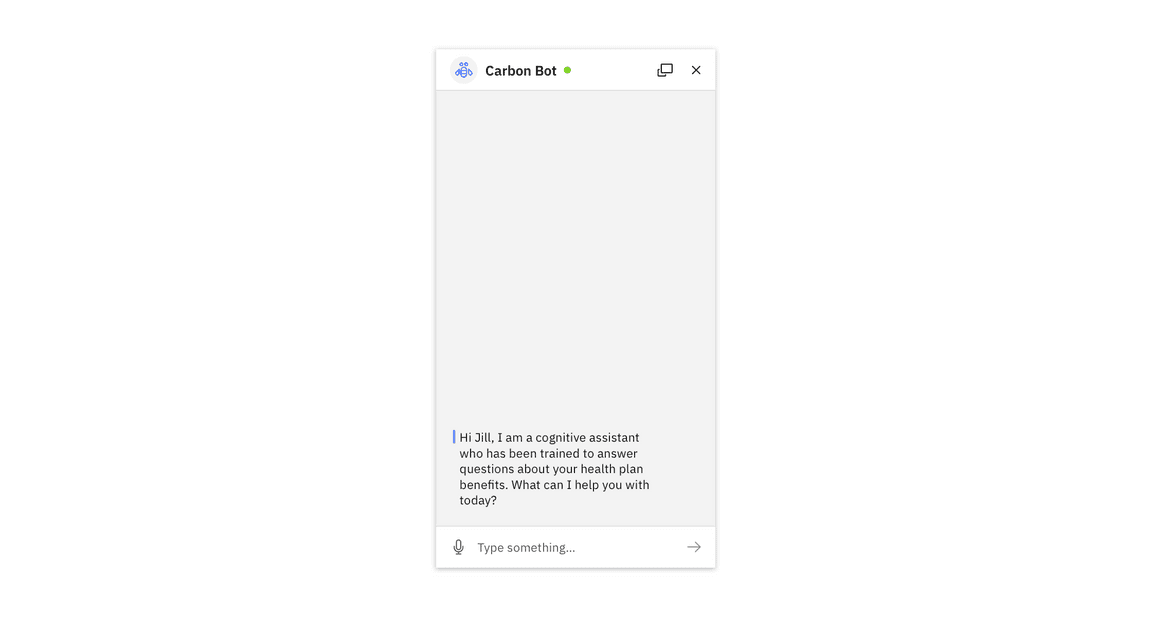
chatbot greeting
User intent
Typically, a user inputs an intent, which can be request for information or a task for the bot to complete. This can take the form of a text (shown here) as well as a structured response (see next section)
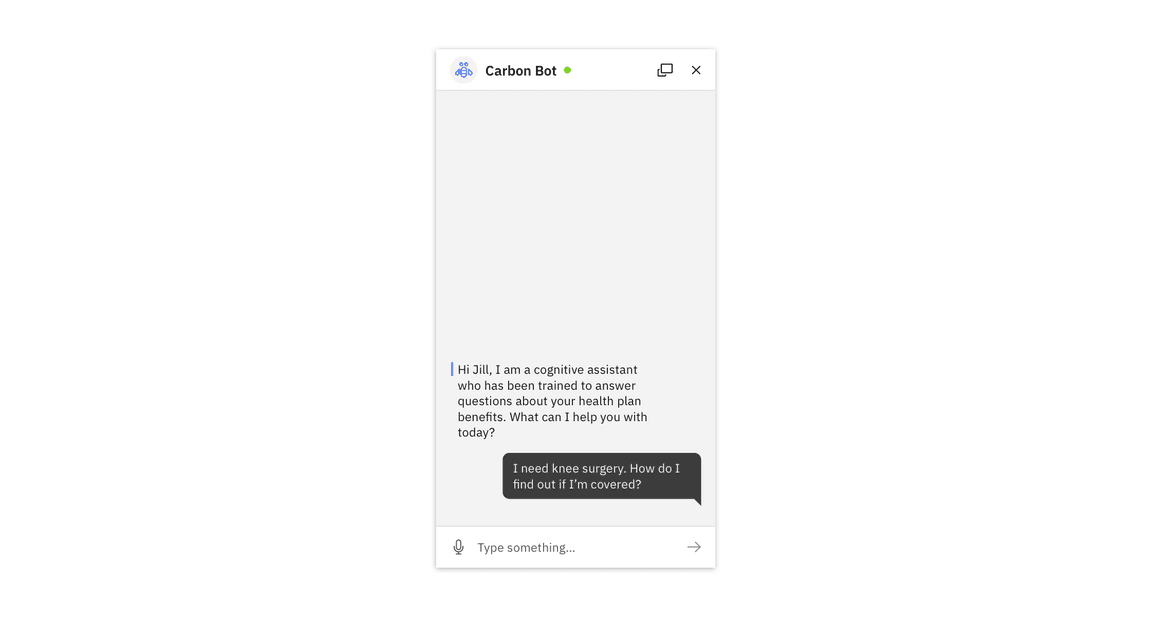
User intent
Structured responses
Prompt for additional details with a menu of structured responses. This narrows the scope to more specific information to answer the user’s question.
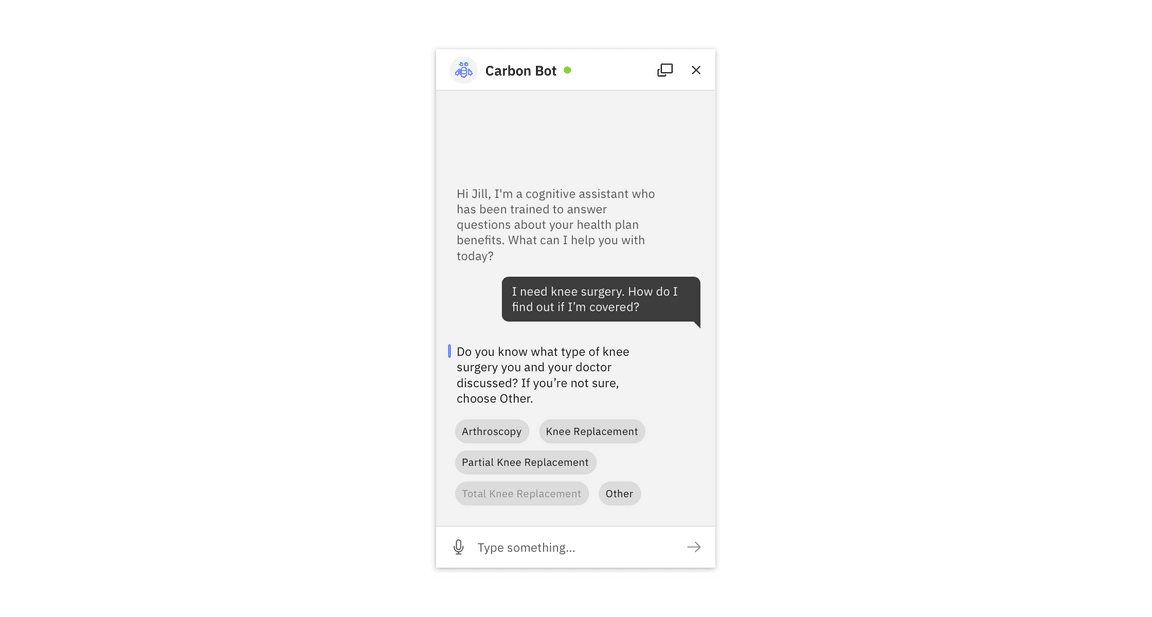
Structured responses
Reflection
The bot should reflect its understanding of the query in the response (when appropriate) to ensure understanding, or before performing a significant action. Note: This process of slotfilling may need to be repeated until the bot has all the information required to answer the user’s initial question.
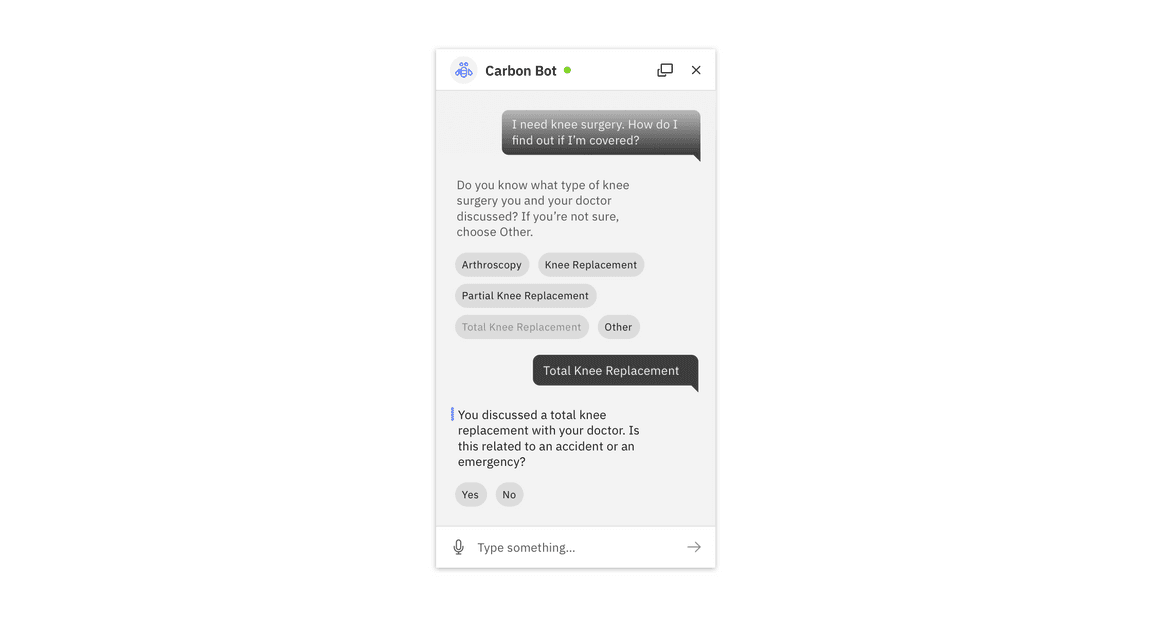
Reflection
Provide a response and request feedback
The bot should provide a thoughtful, informative response to the user’s intent, based on the information they have provided throughout the conversation. When appropriate, be sure to provide an opportunity for users to give feedback. Consider allowing the user to input a custom response. Provide an opportunity for users to give feedback where possible. Consider allowing the user to input a custom response.
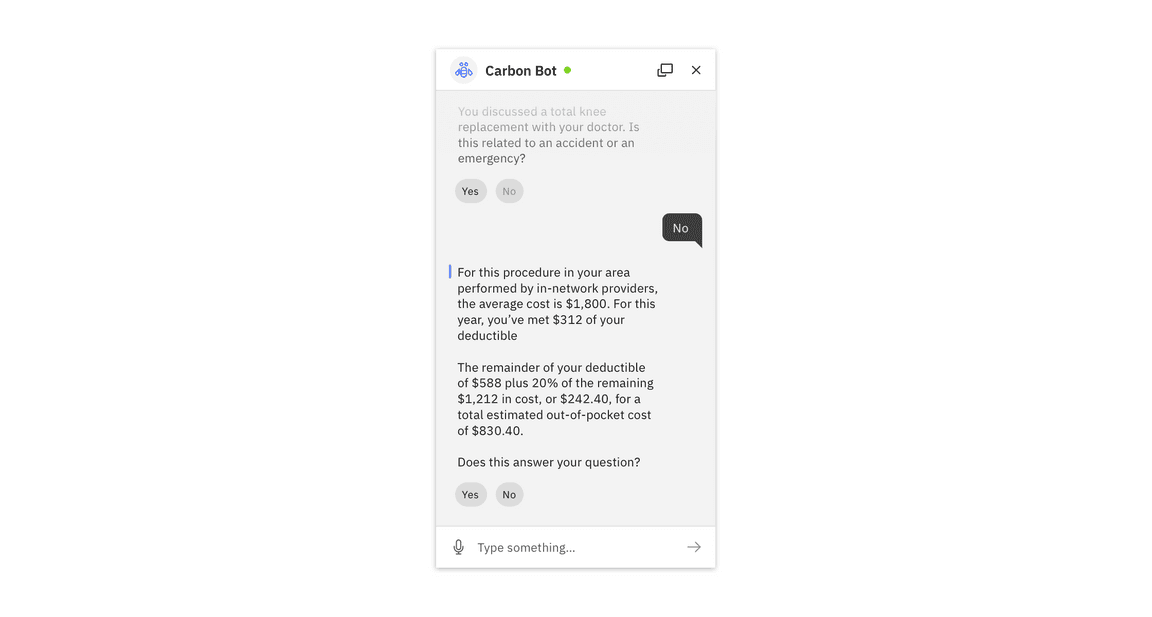
Provide a response and request feedback